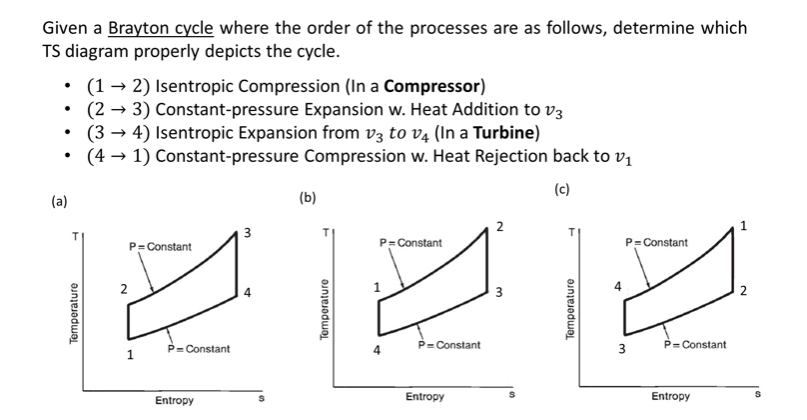
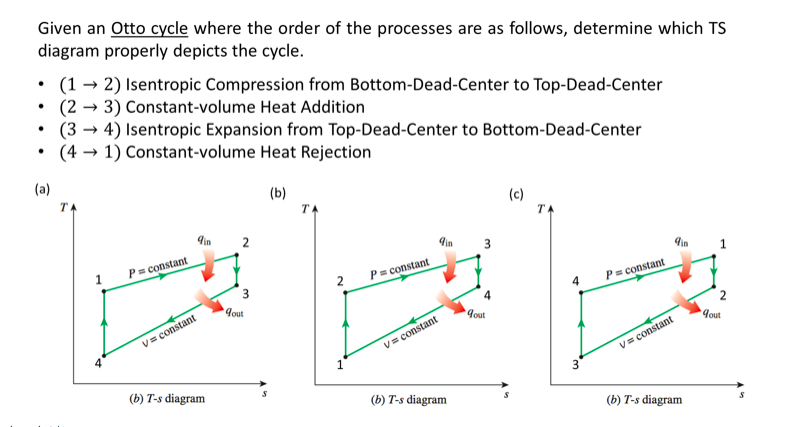
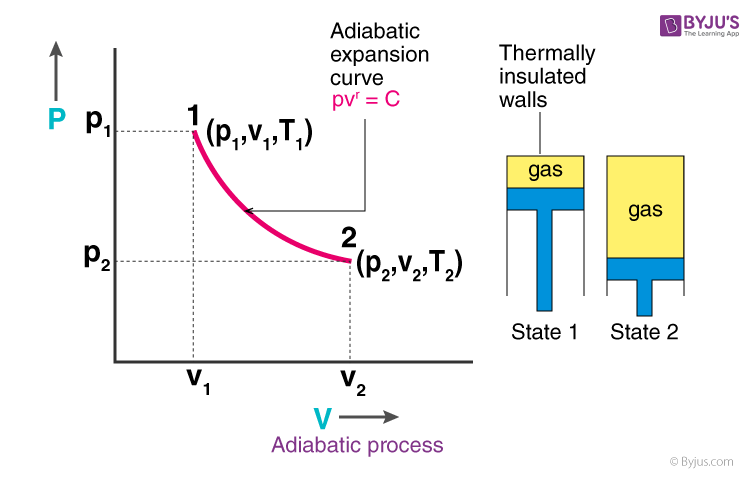
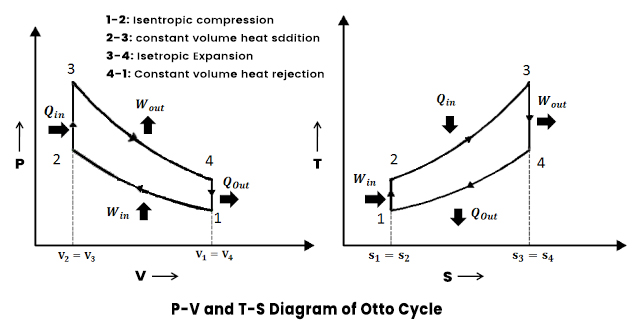
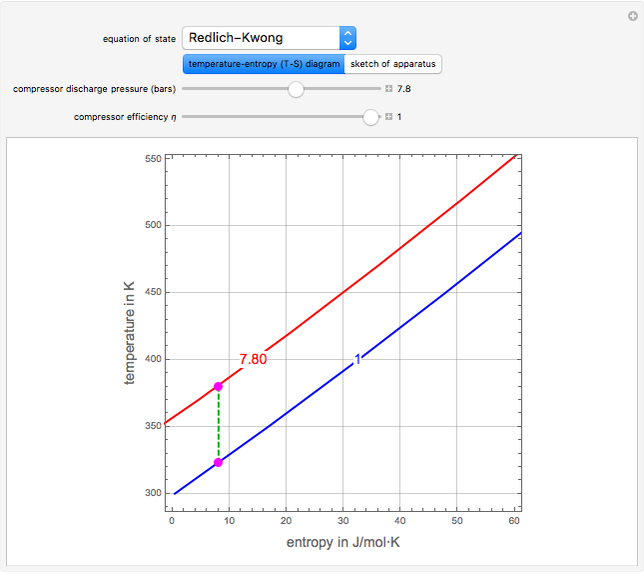
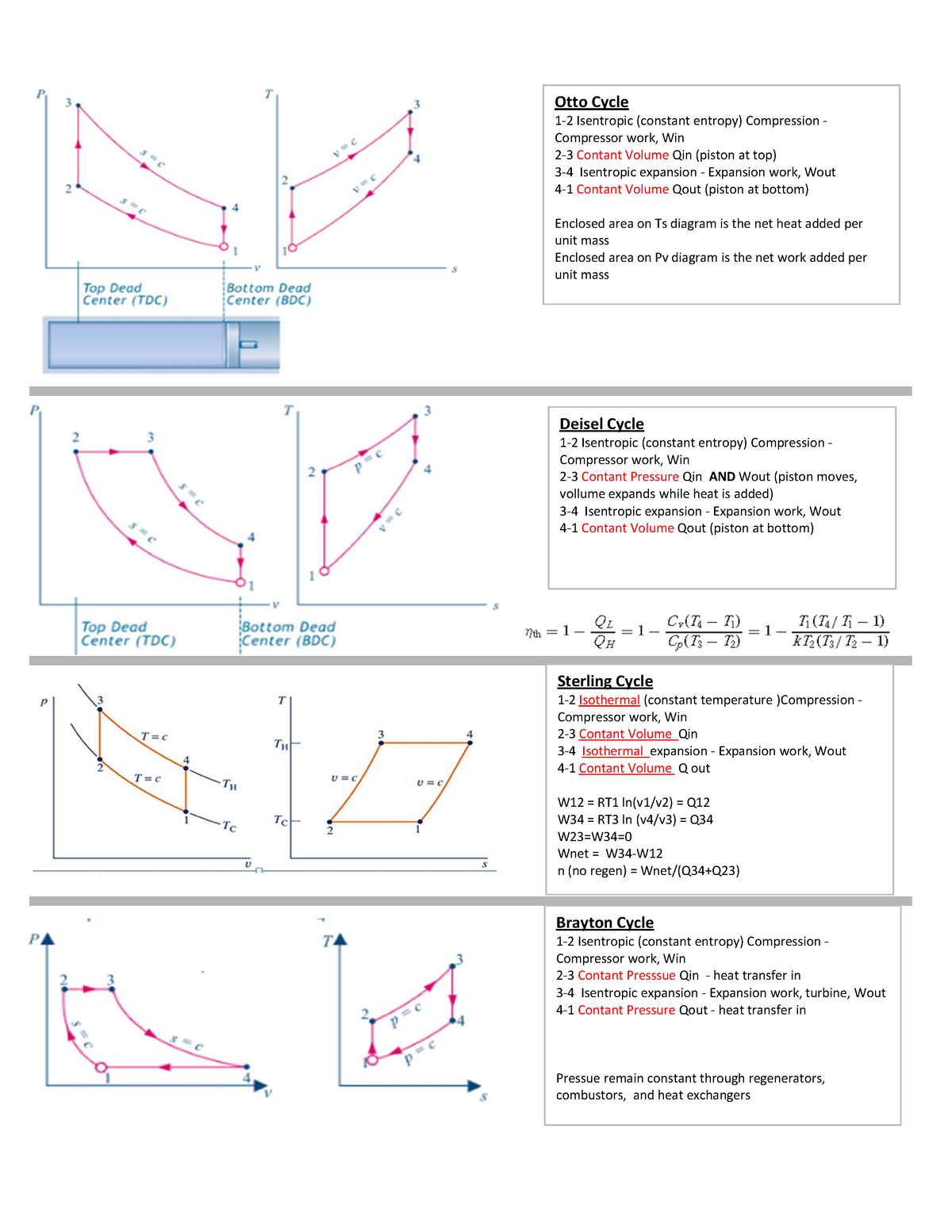
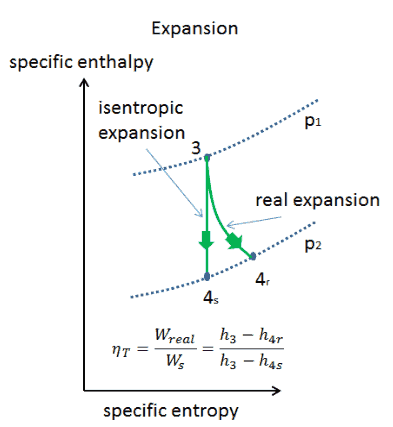
Isentropic Compression Ts Diagram
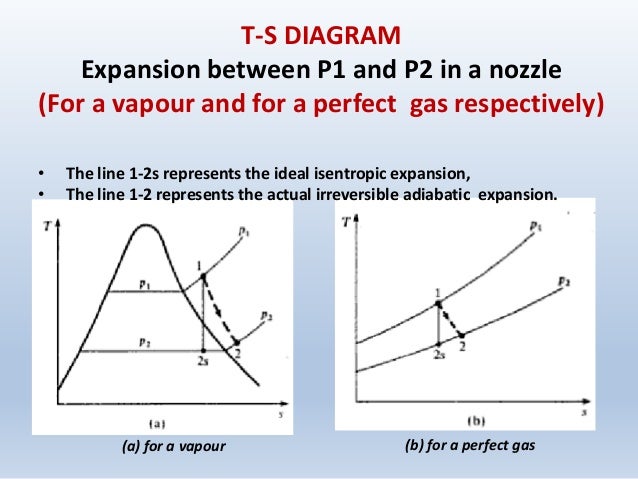
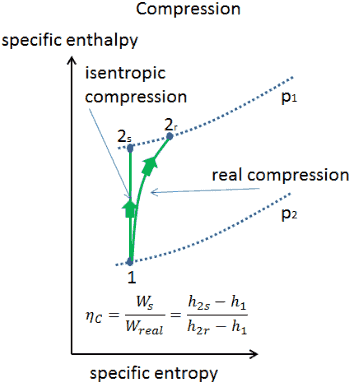
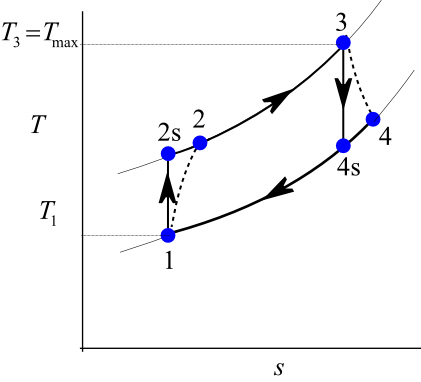
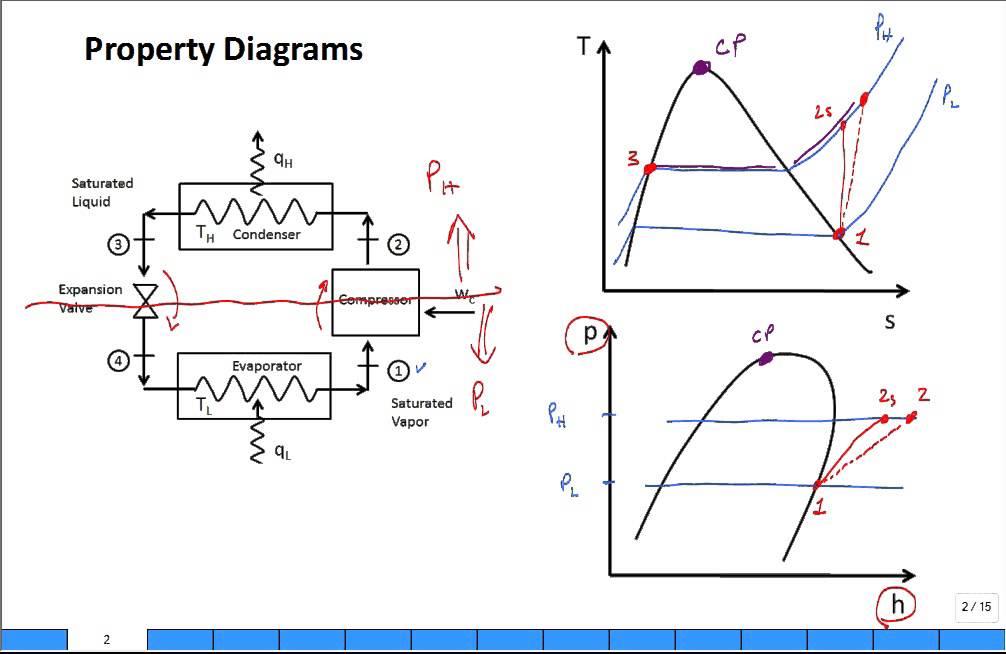
The parameter that describes how efficiently a device approximates a corresponding isentropic device is called isentropic or adiabatic efficiency.

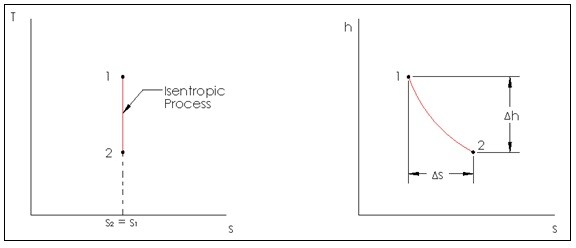
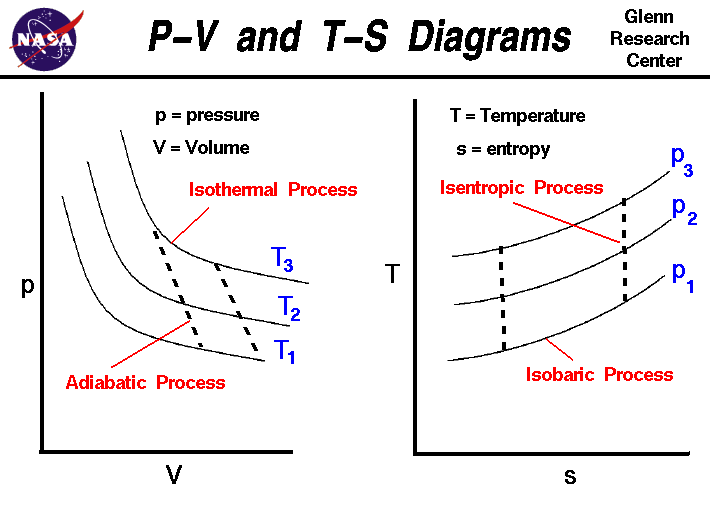
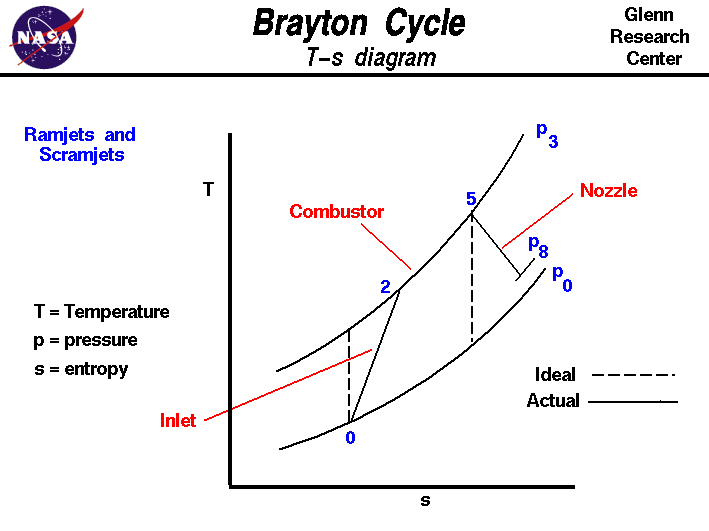
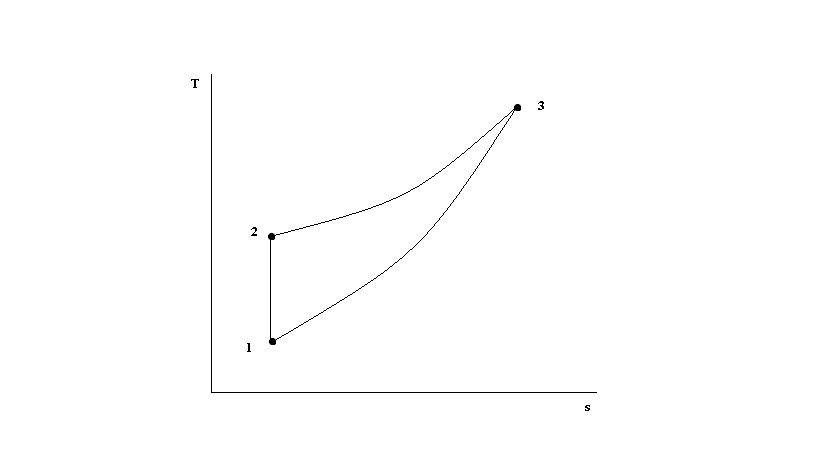
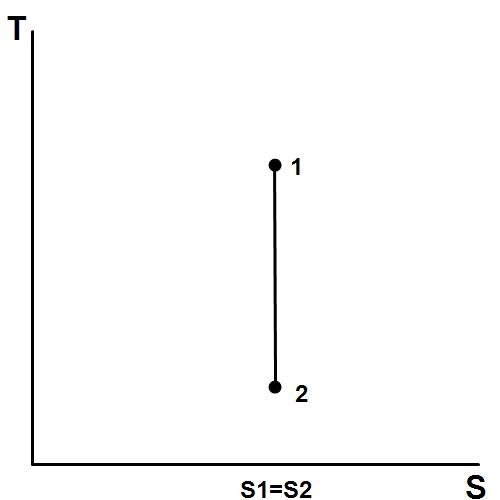
Isentropic compression ts diagram. Assume an isentropic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbinesince helium behaves almost as an ideal gas use the ideal gas law to calculate outlet temperature of the gas t 4isin this turbines the high pressure stage receives gas point 3 at the figure. Isentropic efficiencies of steady flow devices in thermodynamic systems. P 3 67 mpa. An isentropic process appears as a vertical line on a t s diagram.
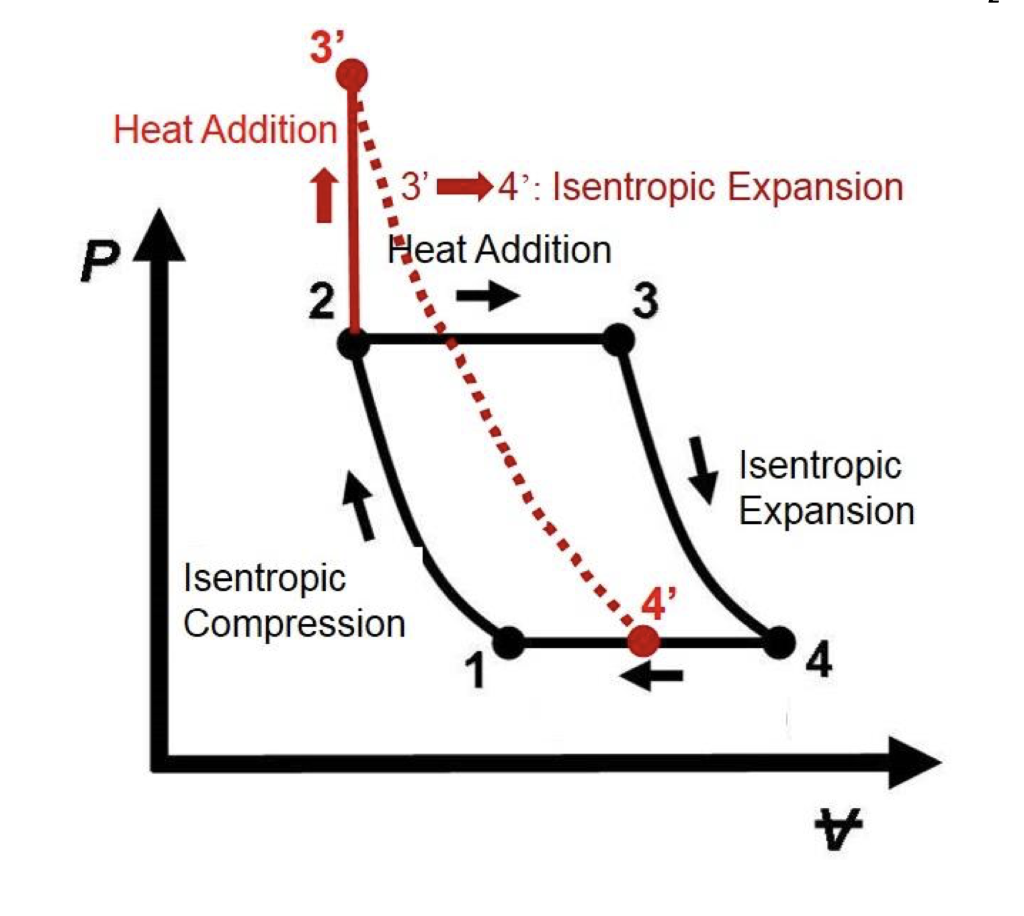
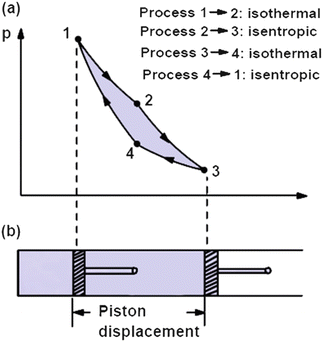
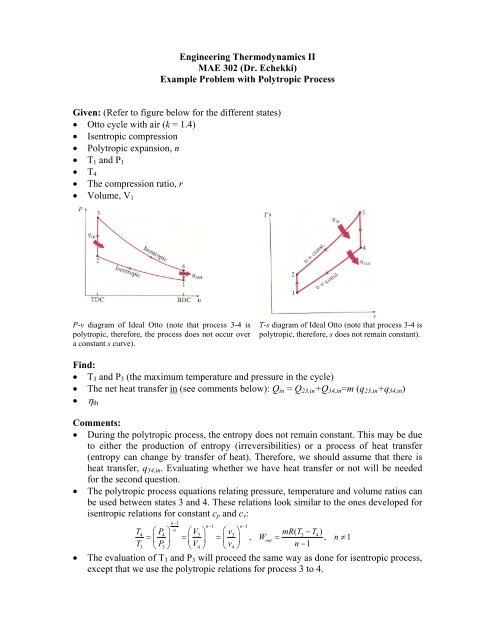
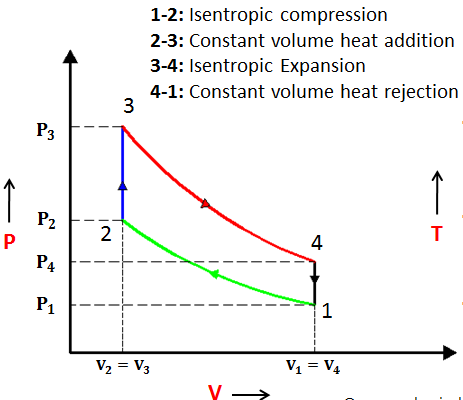
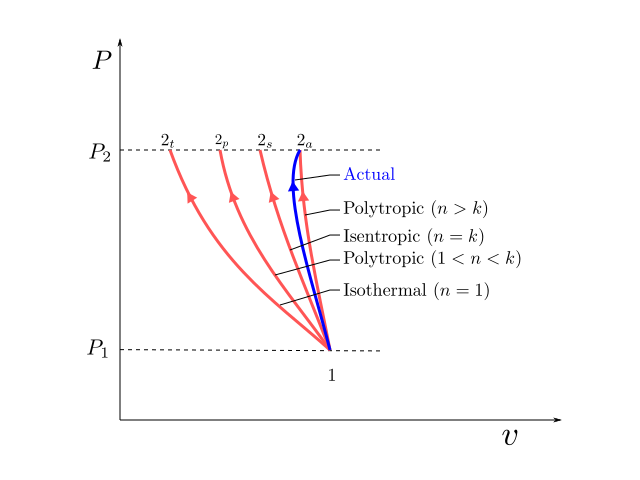
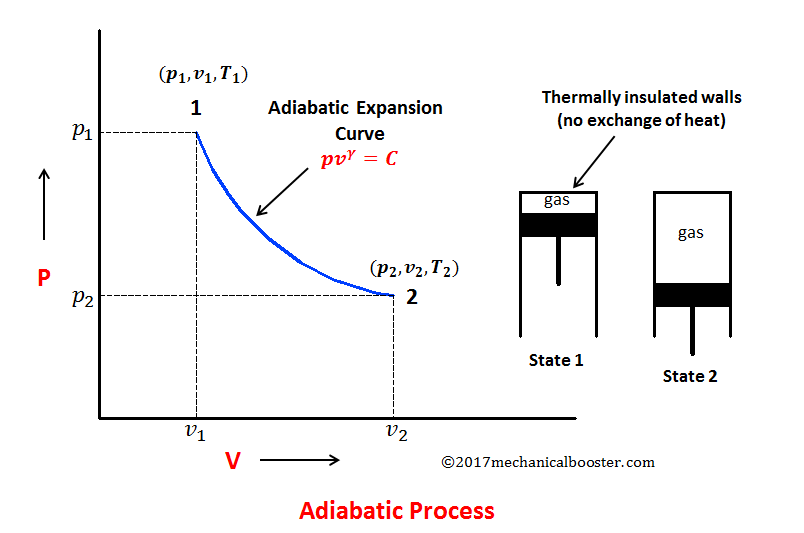
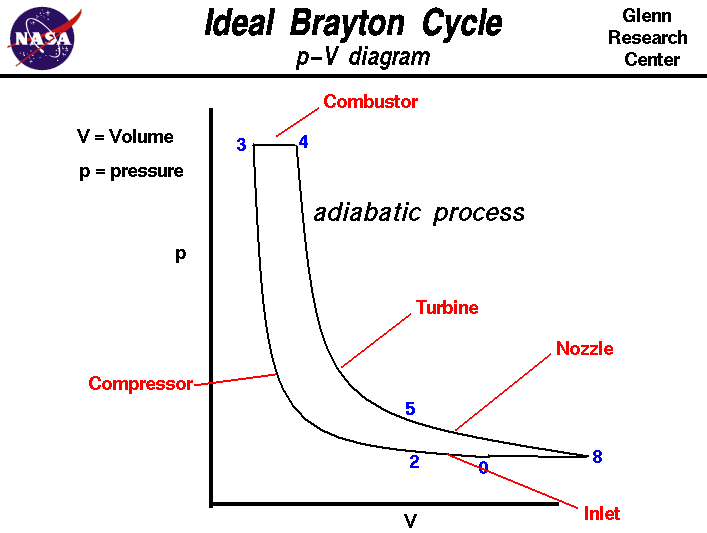
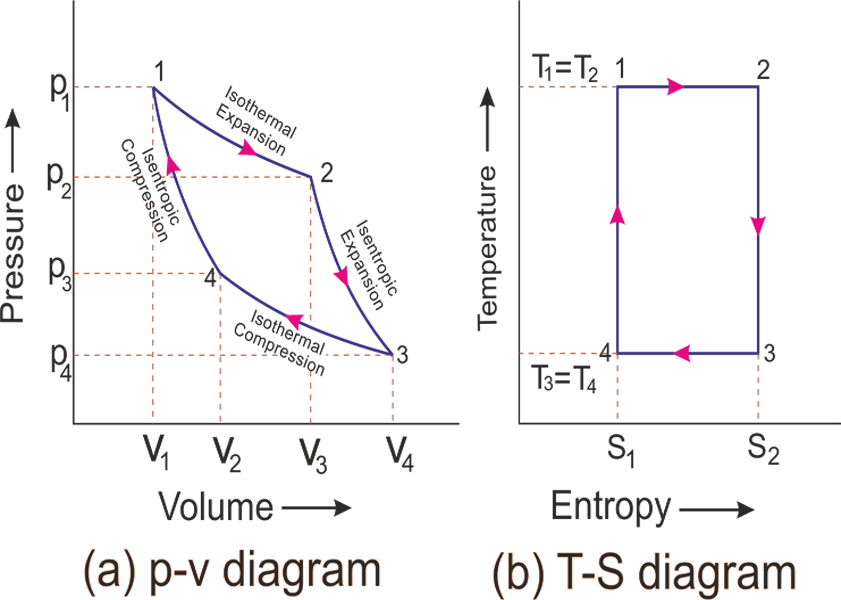
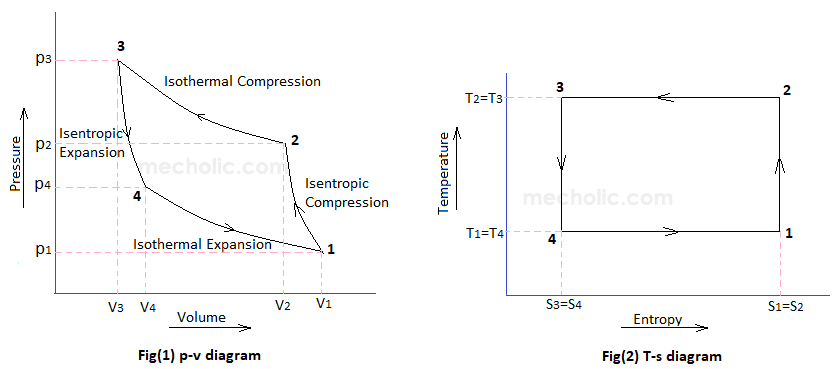
Remember that our system contains an ideal gas with constant heat capacities and therefore a constant heat capacity ratio. It is possible to perform a series of processes in which the state is changed during each process but the gas eventually returns to its original state. Isentropic expansion in gas turbine p v diagram of an isentropic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbine. The compression process may be isentropic polytropic or isothermal let p 1 suction pressure pressure before compression v 1 suction volume t 1 suction temperature p 2 v 2 t 2 are the corresponding pressure volume and temperature after compression.
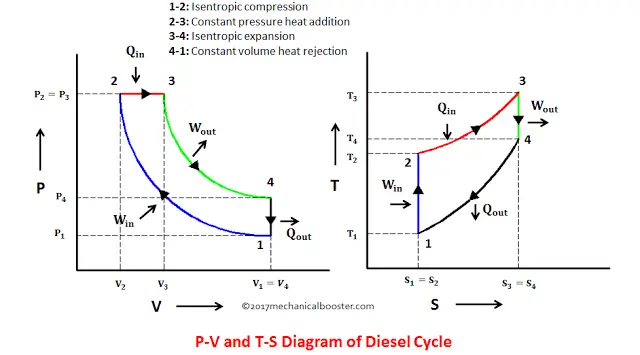
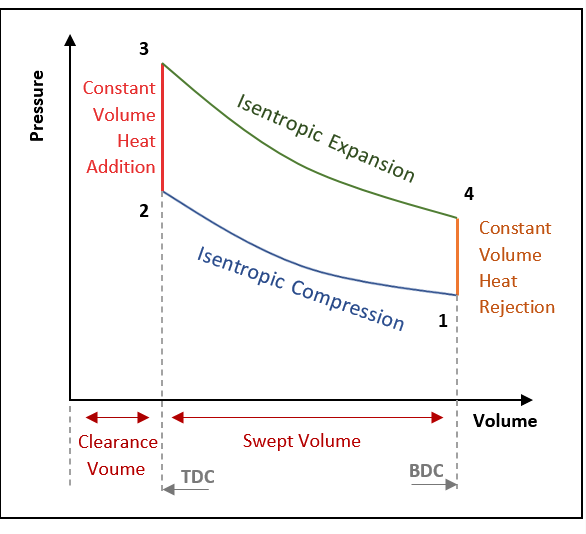
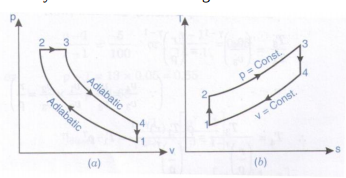
This isothermal compression is represented by the curve 3 4 on p v and t s diagram. In this process the piston moves from bdc to tdc and compression of air takes place isentropically. Ch 7 lesson e page 9 isentropic process paths on pv and ts diagrams. P 3 67.
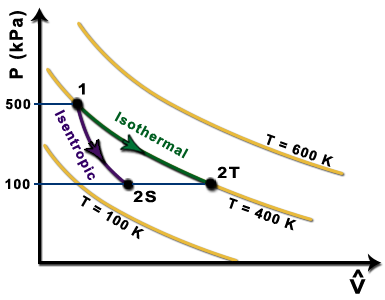
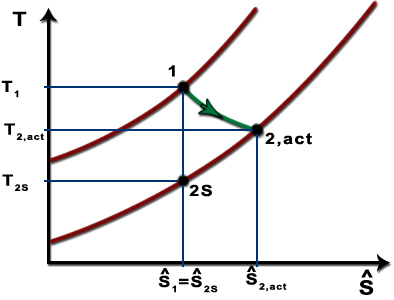
R is compression ratio p 1 p 2. Initially this page shows a pv diagram. It would be seen that during this process the heat is rejected to the cold body and is equal to the work done on the air. As the temperature increases from t 2s to t 2act along the 05 mpa isobar the specific volume must increase right.
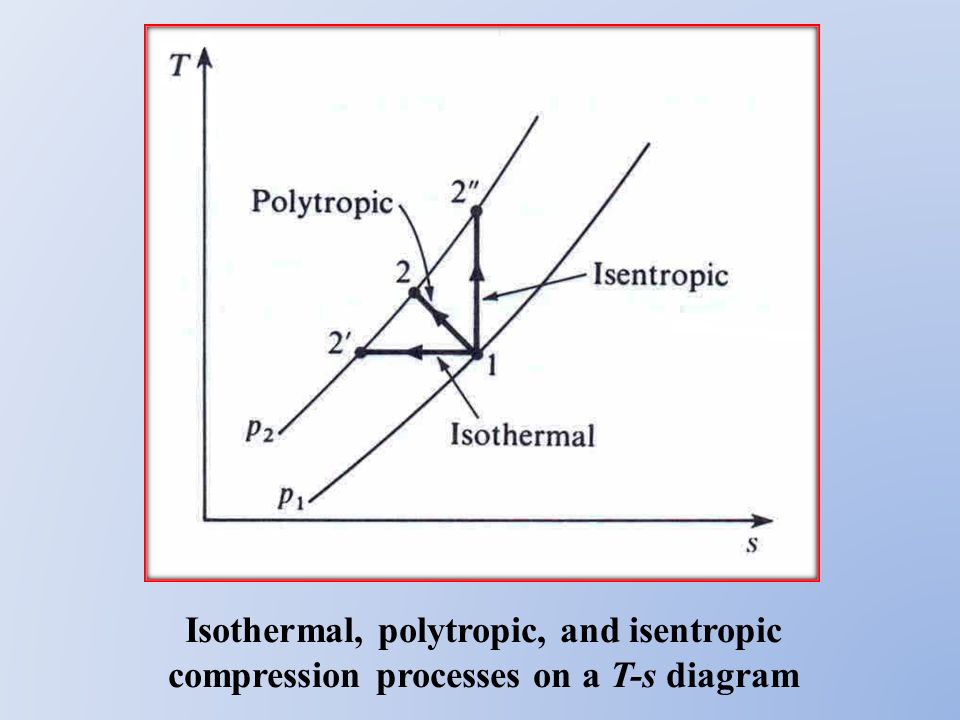
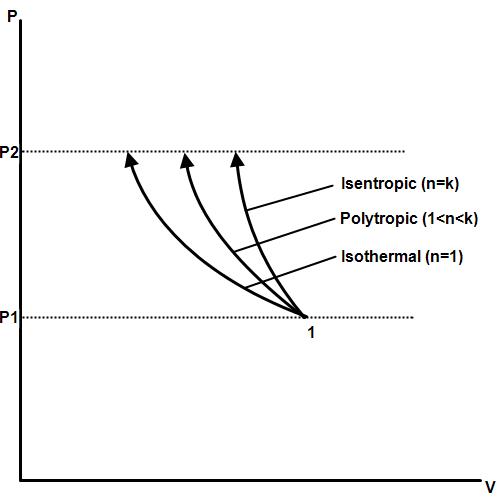
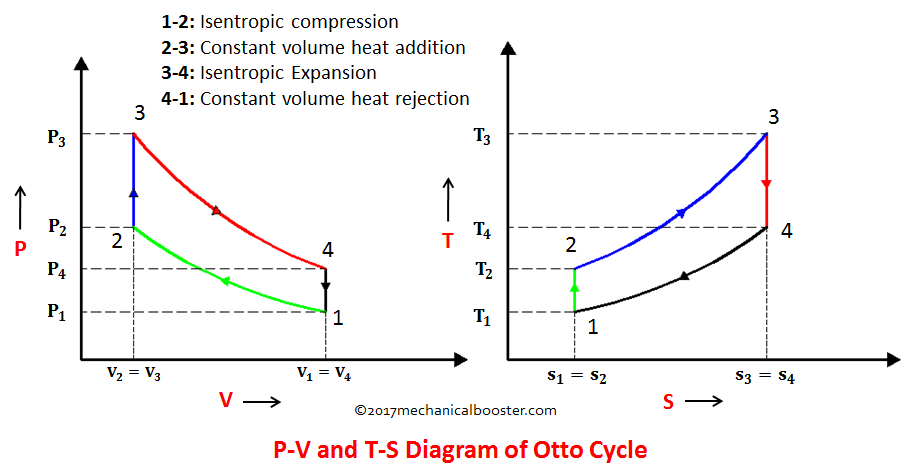
Assume an isentropic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbinesince helium behaves almost as an ideal gas use the ideal gas law to calculate outlet temperature of the gas t 4isin this turbines the high pressure stage receives gas point 3 at the figure. Lets begin by plotting an isentropic process path on both a pv and a ts diagram. T 3 1190 k 9170c from a heat. In this diagram the path 2 3 represents the polytropic compression and the path 2 3 represents the isothermal compression and the path 2 3 represents the isentropic compression.
From the above diagram it is clear that the air is drawn in by the cylinder during the suction stroke 1 2. P v diagram of an isentropic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbine. Hear rejected work done on the air. The following figure shows the pv and ts diagram of this compressor.
Well you can see from the ts diagram that some of the excess energy is converted into internal energy resulting in an increase in temperature. It means that during compression the entropy remains constant and there is no flow of heat out of the cylinder walls non conductors happens.