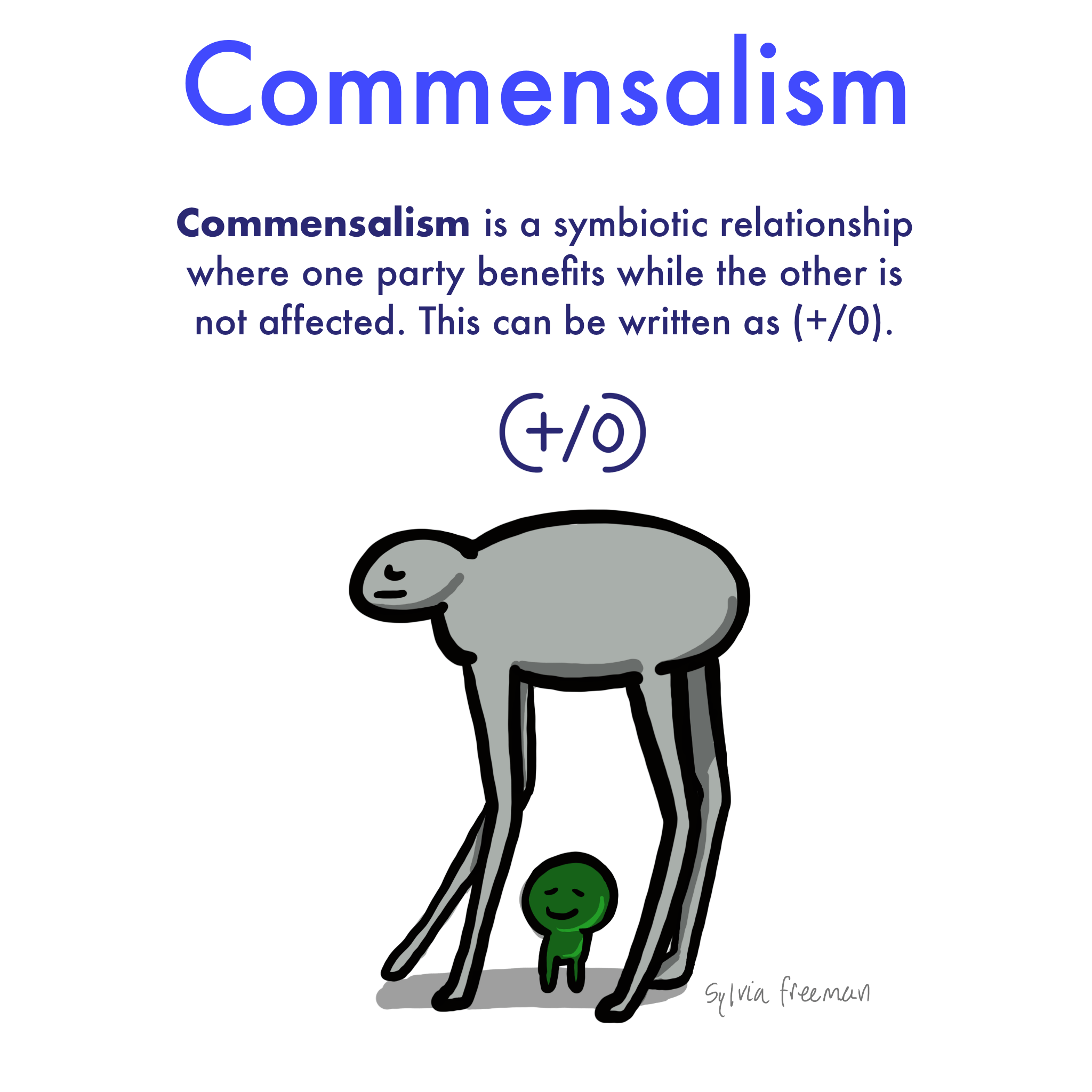
Commensalism Symbiosis
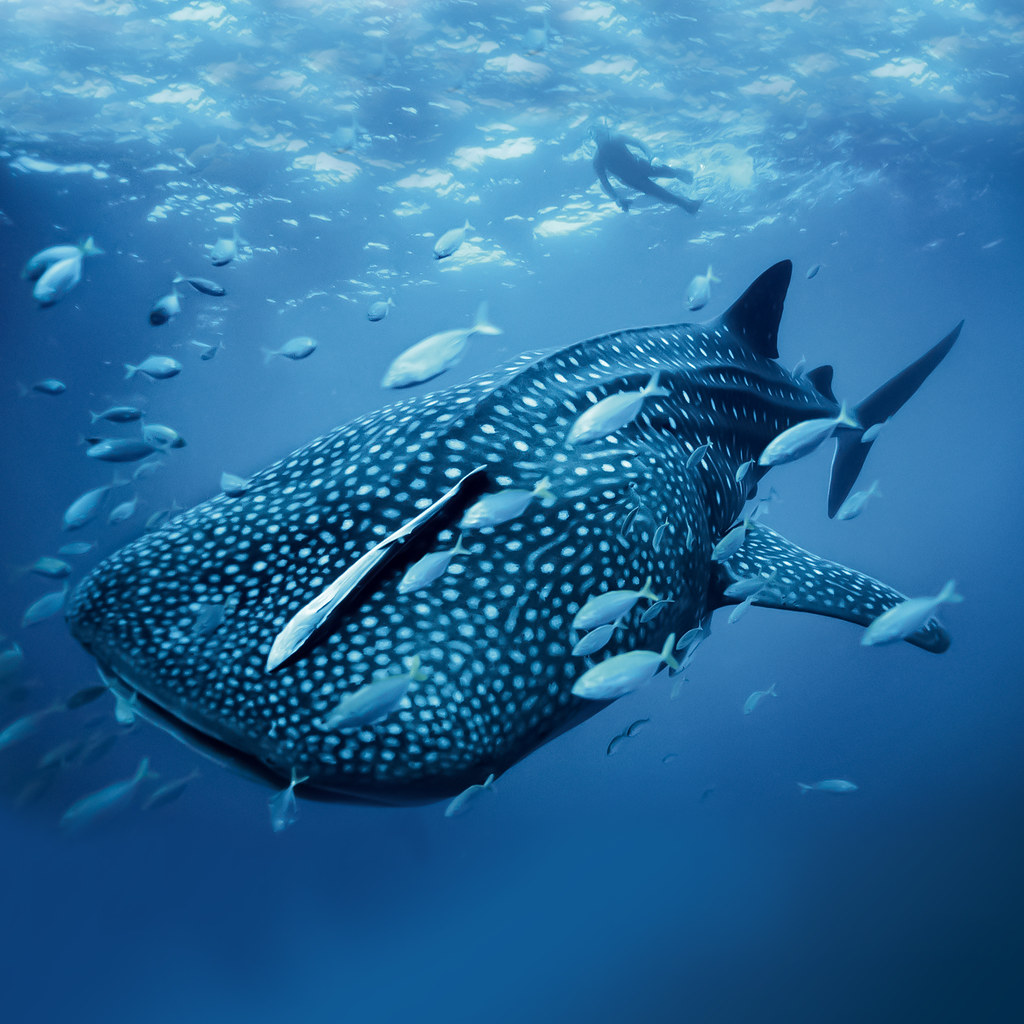
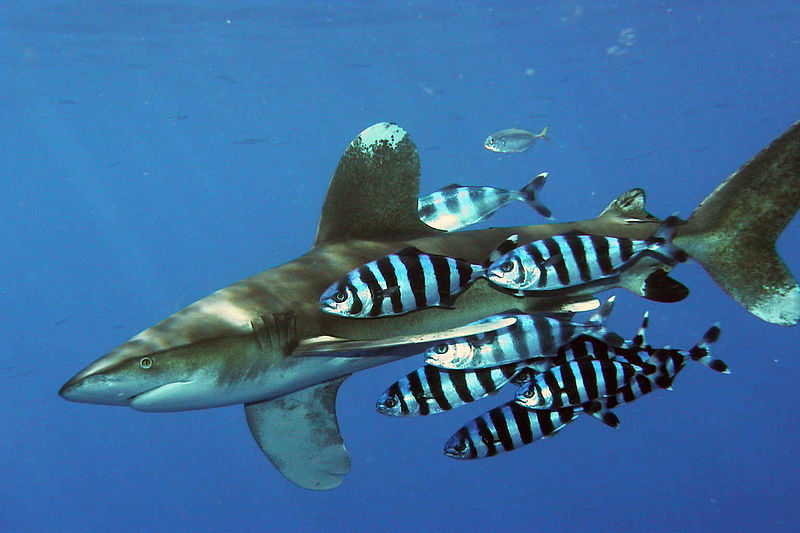
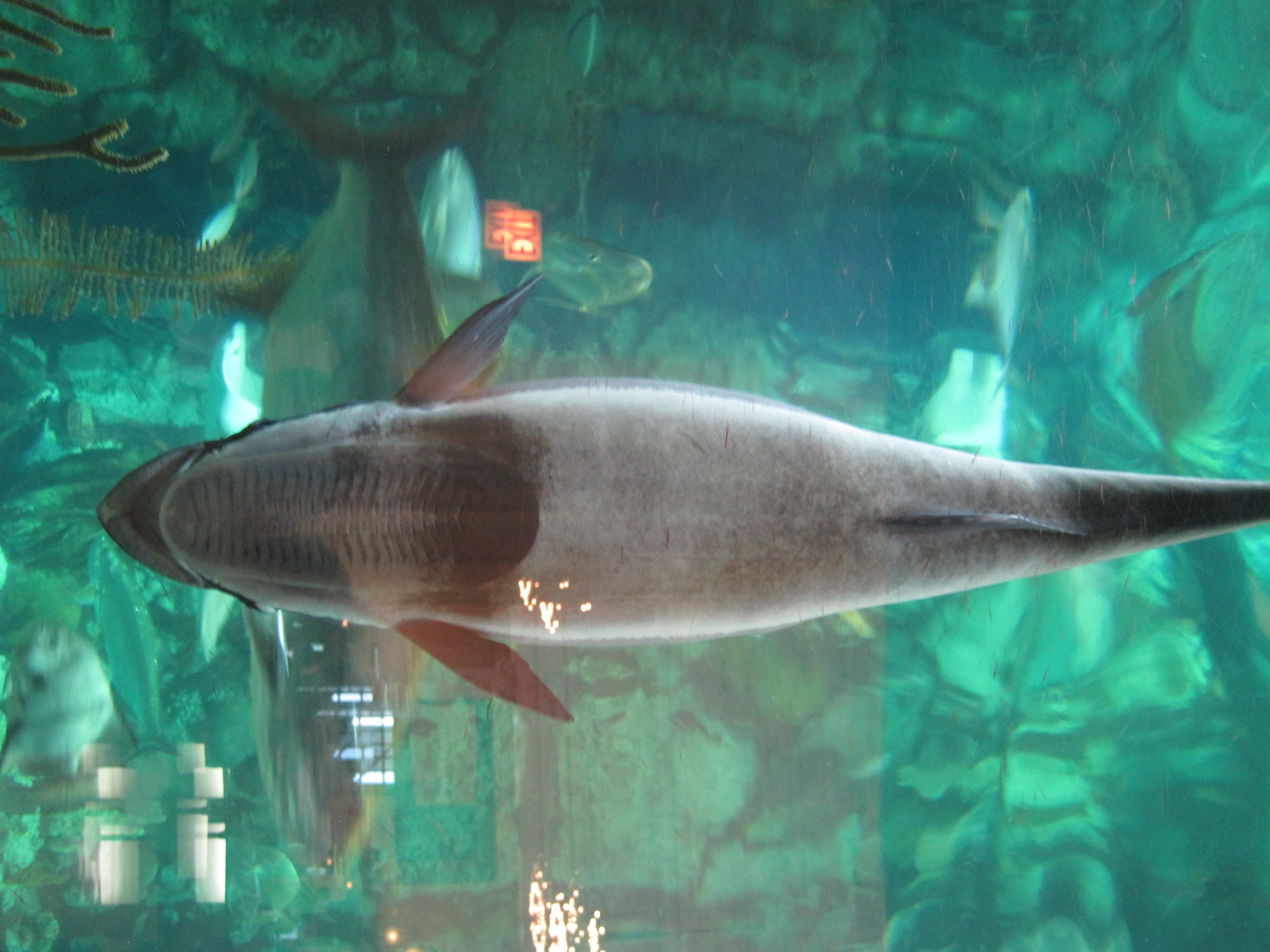
Remoras have evolved on the top of their heads a flat oval sucking disk structure that adheres to the bodies of their hosts.

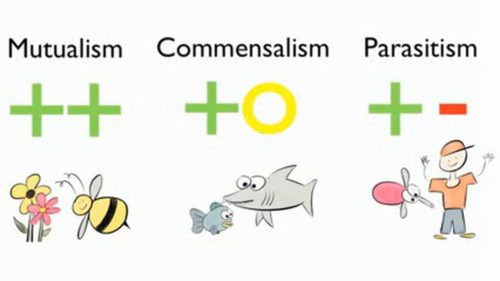
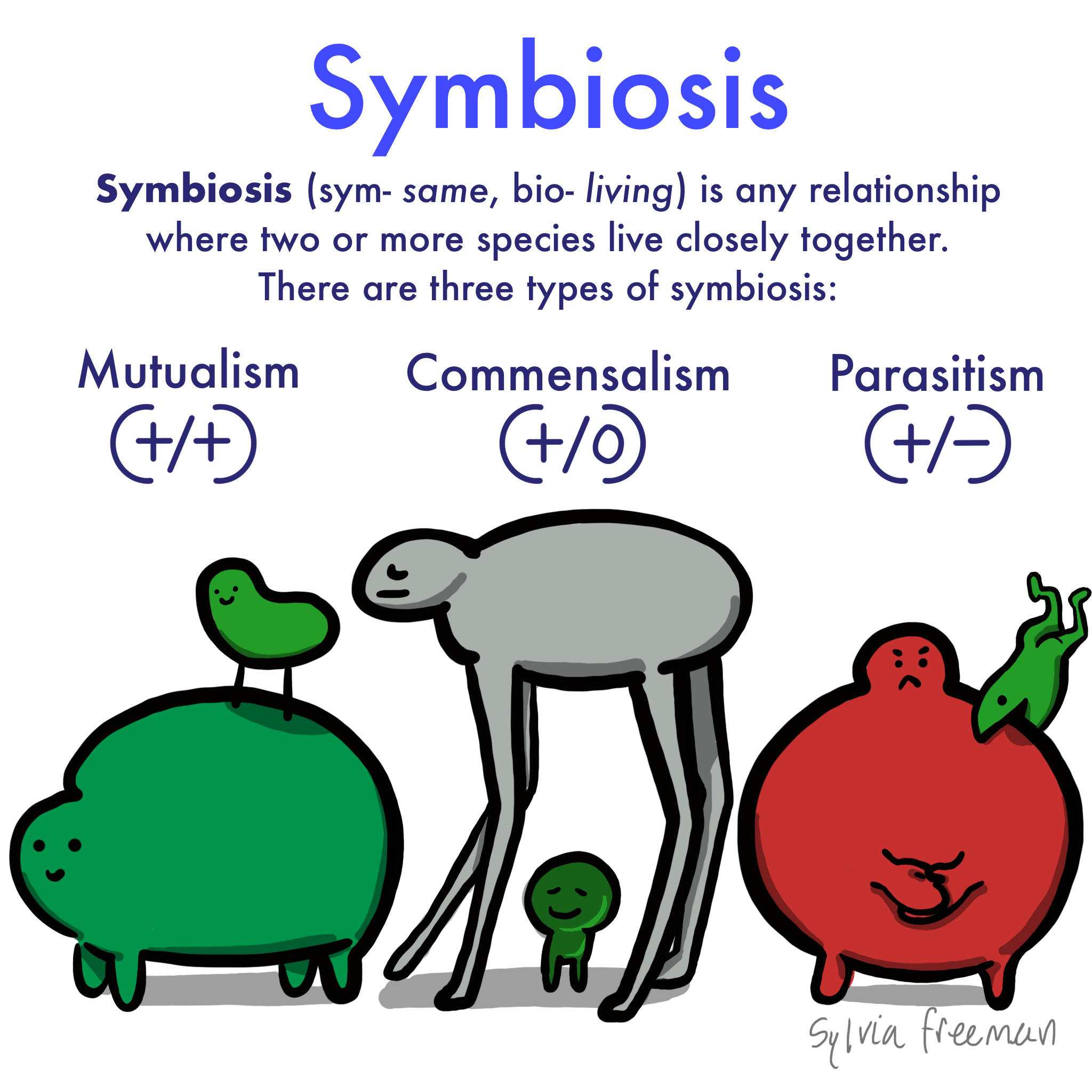
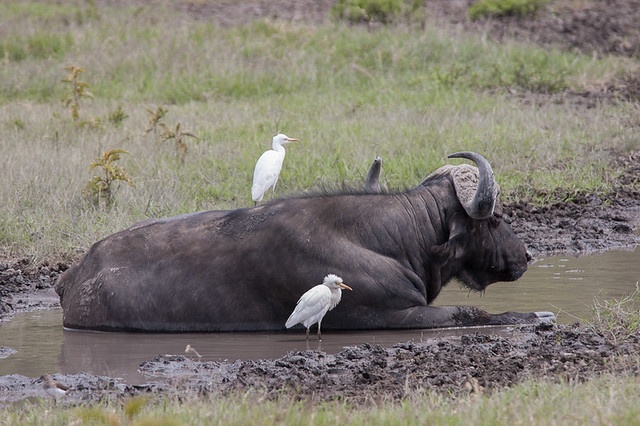
Commensalism symbiosis. Commensalism can either be a brief interaction or a lifelong symbiosis. One way that organisms are symbiotically interlinked is called commensalism which occurs when one species benefits while the other is unaffected. For instance hermit crabs make their home in the shells of dead snails. Mutualism is where both organisms benefit commensalism is where one benefits but the other organism isnt harmed and lastly parasitism is where one organism benefits and the other is harmed.
Commensalism is a type of symbiosis. The species that gains the benefit is called the commensal. Symbiosis is broken down into mutualism commensalism and parasitism based on how two species interact in their ecosystem. Commensalism being a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms other types of symbiotic relationships include mutualism in which both the organisms involved benefit from each other and parasitism where one of the organisms is benefited while the other is harmed.
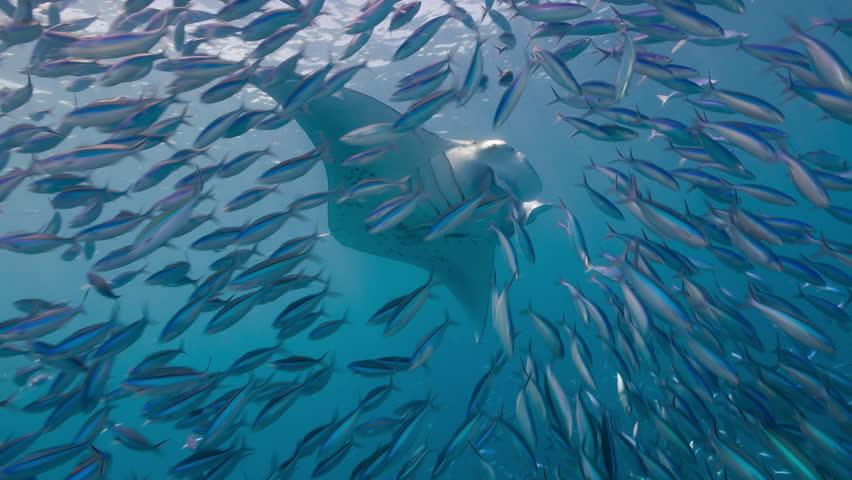
One of the best known examples of a commensal is the remora family echineidae that rides attached to sharks and other fishes. The commensal organism obtains food shelter locomotion or support. Symbiosis refers to any long term interaction that two organisms have with each other. Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while the other species is neither harmed nor helped.
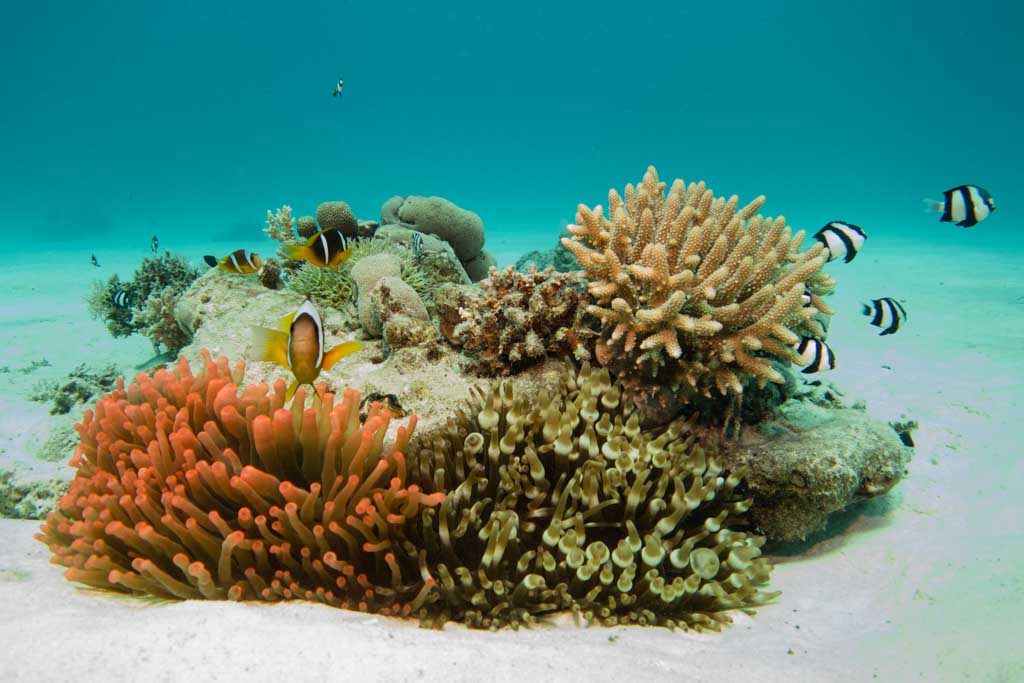
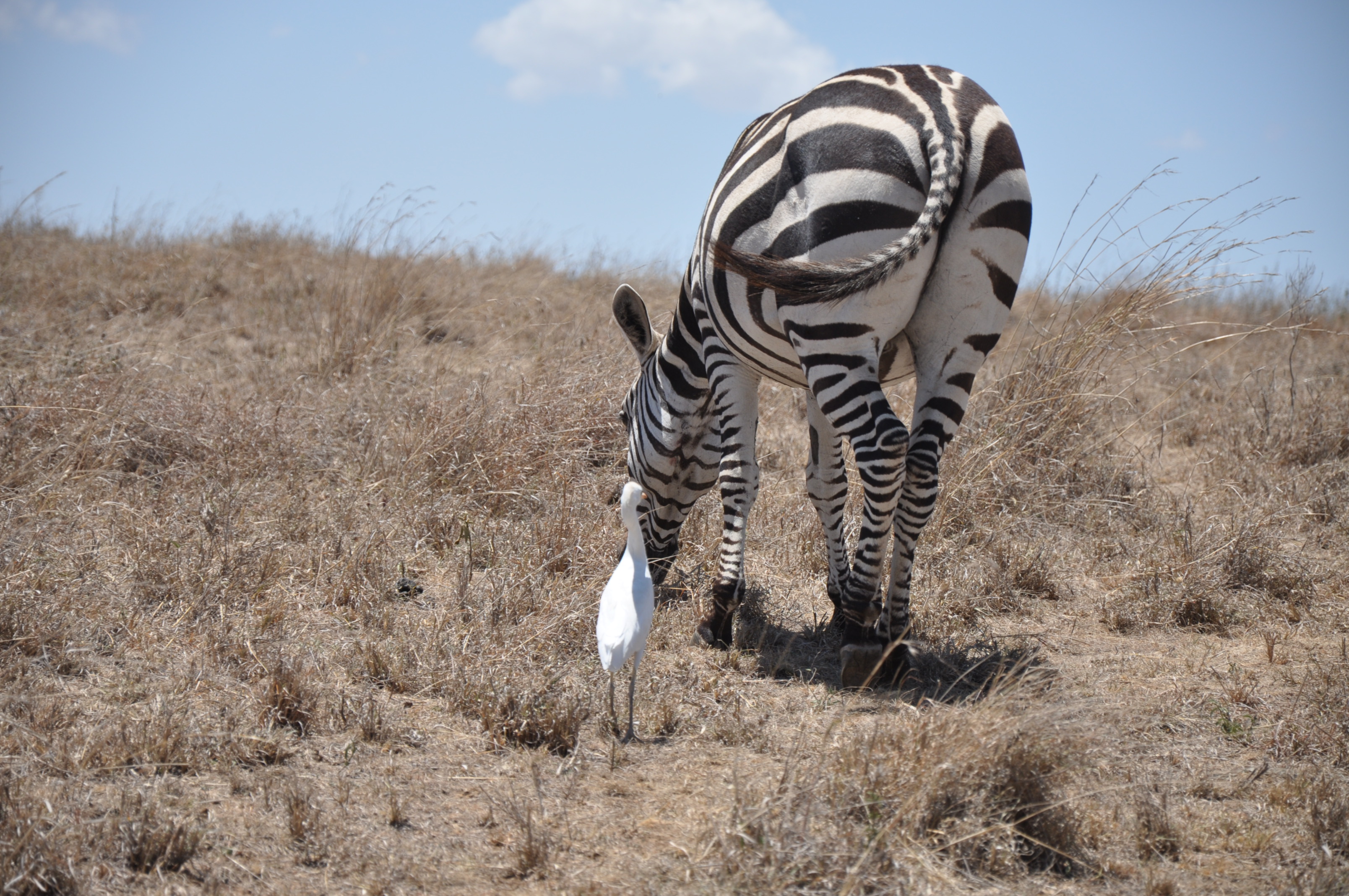
In a commensal relationship one organism benefits while the other is generally unaffected. A hyena and lion who get into a fight then never see each other again would not qualify to be living in symbiosis because their interaction is not long term. Living organisms are bound together in a web of relationships that can be helpful harmful or inconsequential to their survival. Commensalism which literally means to eat at the same table thanks latin is one form of symbiosis a relationship between two organisms of different species.
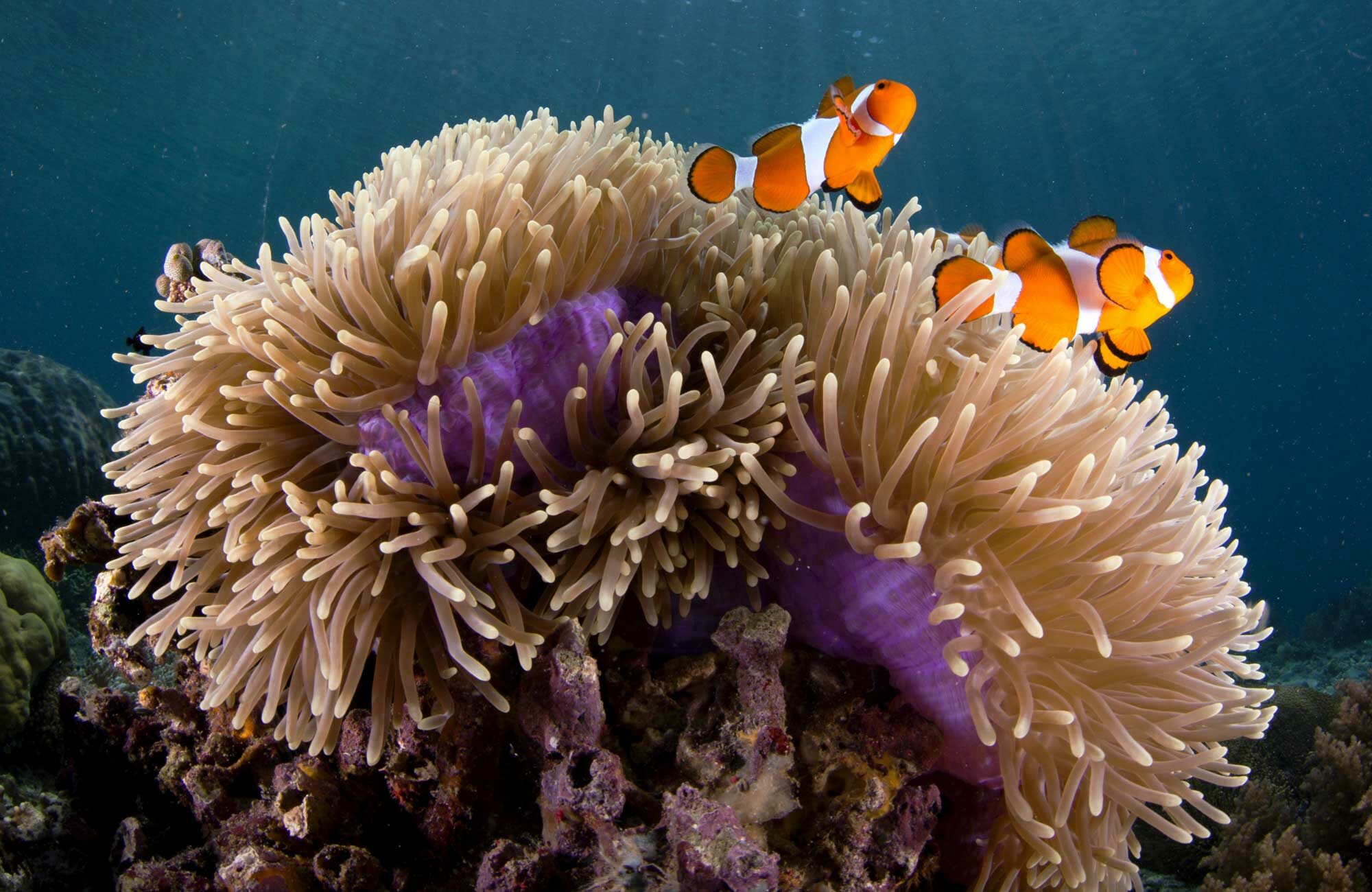
Monarch butterflies and milkweed are an example of commensalism. The other species is termed the host species. This relationship can be contrasted with mutualism in which both species benefit.













.jpg)









.jpg)




































.jpg)





















/commensalism-definition-and-examples-4114713-v2-706cadecce404b008d6620bb061841cc.png)